Google Announces Free Product Listings on Google Shopping
How to create a Google Shopping feed
Google Shopping is quickly becoming the single largest repository of product information. In May of 2020 Google started accepting organic listings for the first time in 8 years creating a significant new organic landscape for eCommerce sites.
This document outlines the steps to take in order to create a Google Shopping feed. At the end of the day the organic winners will be those sites that invest in original content that engages and converts the reader but the first step is to make sure that Google has full visibility to your product catalog.
Here’s the information you’ll want to add to your feed:
- ID: A unique alphanumeric ID number for every product you sell.
- Title: This may be the single most important element on the page in terms and should include the most important keywords.
- Description: Google will accept up to 5,000 characters in the description and again it’s important to integrate the appropriate keywords that will match your customers’ search queries.
- Link: A link to the product URL on the site.
- Image link: Google wants the link so that it can easily display your photo within the search results. Use the primary image.
- Price: It’s important that you deliver the feed frequently and that the price on your feed matches the price on your site. Assume that Google is checking.
- Brand: This is the brand name of the product and it helps Google match search intent to the product.
- GTIN: If available, include the Global Trade Item Number. This helps Google to group sellers of the same product. Google can help you find your item’s GTIN if you’re unsure.
- Shipping Weight, Length, Width & Height: Google Shopping tries to estimate the total cost of shipping. Values like weight, and shipping dimensions are designed to work alongside your shipping settings inside of Google Merchant Center.
- Sales Tax: This is required in the US only if needed to override the account tax settings for an individual item. Use Google Merchant Center to settings to maintain your overall sales tax information.
Is my site eligible for Google Shopping?
Yes! All retailers can opt-in to show their products across Google Shopping for free once the product feed is submitted to the Google Merchant Center. Keep in mind that Google does restrict listings for illegal, regulated, or sensitive products.
How do I get to page one of Google Shopping?
The feed is critical and serves as Google’s starting point, but frankly that’s just a ticket to the game. In order to get to page one, you’ll have to compete for the best and most relevant product listings against all the other providers with products relevant to the search. Here’s a list of things to consider.
- Perfect your product title: The product title may be the most important page element and is weighed heavily in Google’s ranking algorithm. Be sure to optimize the title around the keyword phrases your customers will use to search for the product. You may need to try a few different titles if you aren’t getting to page one.
- Test different images: An image can really help your product stick out on a busy SERP, so pay attention to your product photography and understand how to stand out relative to other photos on the SERP.
- Provide as much product detail as possible: While the most important keywords should be in your title, the description is an opportunity to connect with a broader range of search queries. Include as many relevant feed attributes as you can , such as your product category, product type, color, condition, size, and color!
- Product Schema: Schema on your website allows search engines to better understand your page. You’ll need to include the required attributes like price, and you can also add reviews to this schema to show the average rating. This can help entice clicks.
Must Have Schema Elements
We have seen in the competitive analysis that most of the eCommerce stores are not using rich snippets effectively. Rich snippets are missing or major product elements are not included in most of the product pages.
The most important details related to a product (which can grab the customer attention) are as following:
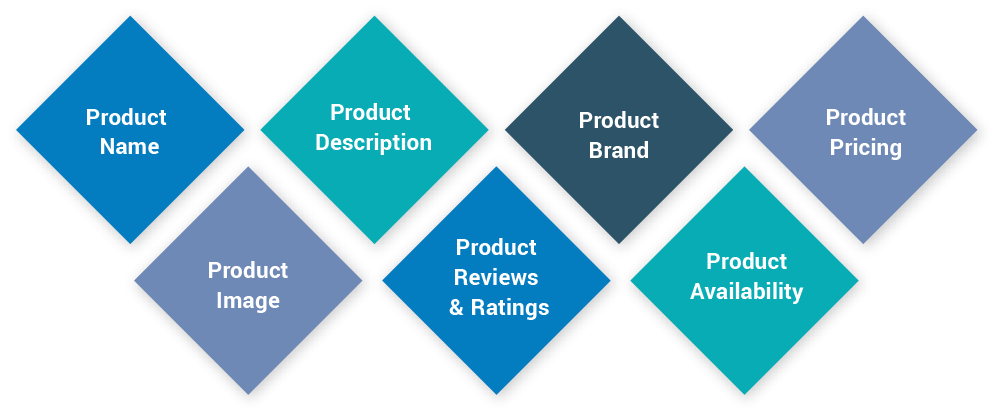
eCommerce stores should consider implementing all important Schema Markups to all the product pages.
5. Offers: If you offer free shipping, or the product is on sale, include this information in the shopping feed. This will help the products stand out from its competitors.
6. PayPal: Google now has a partnership with PayPal, to quickly help stores with set up and provide users with “high quality results”. If you need a faster, more secure payment method for products, this is definitely worth looking into.
How will organic Google Shopping results impact paid product listing ads (PLA)?
Retailers can and should continue to show their paid ads alongside these new free organic listings. This will allow retailers more flexibility in how they chose to promote their full inventory across Google. Once the products are approved in Google Merchant Center, a retailer can create a Google Shopping campaign within Google Ads and promote specific items across Google, paying only when a searcher arrives at their site.
Current Google Shopping advertisers will continue to show their ads on the Google Shopping tab, primarily towards the top and bottom of the pages. Nonpaid (organic) listings will take the remaining real estate within that tab.
The shopping results from the Google Search results page, partner search engines, Google images, the Google Display Network, Gmail, and YouTube will still only feature paid shopping ads at this time, so advertisers won’t expect to lose much of their shopping ads traffic.
What is the ‘Google Buy Button’ or ‘Purchases on Google’?
Google has branded the tool as Purchases on Google but many people refer to it as the Google Buy Button. The buy button appears when people do product-related searches on Android phones or tablets. This is how the process unfolds:
- Google Shopping product listing ads appear on those searches and if one of the advertisers uses Purchases on Google, its ad will have a “Buy on Google” button.
- When the user clicks on the Buy on Google button they go to a landing page on Google, i.e. not the retailer’s website.
- The user can add the product to a shopping cart.
- They then complete the purchase using Google Wallet, all without ever leaving Google.
- The retailer then fulfills the order and is responsible for all communications and interactions with the customer in relation to that order.
At the time of the launch, Google said it had analyzed conversion data and found the conversion rates for its Product Listing Ads were 50 percent lower on mobile than desktop.
With the Google Buy Button, Google aimed to increase conversion rates on mobile. Google says its buy button simplifies the process of buying online as the purchaser already has an account with Google and a method of payment.
This is easier than going to a retailer’s website and, potentially, creating a new account and/or entering delivery and payment information.




